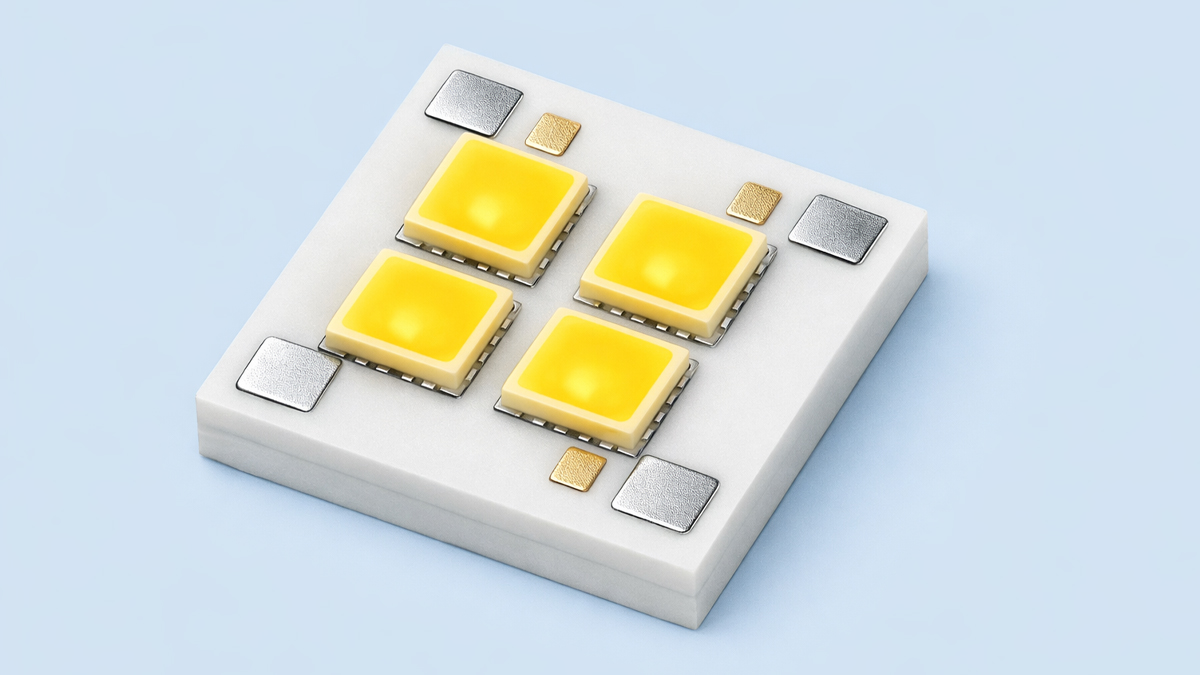
What is Flip Chip LED?
Flip Chip LED is an advanced form of light emitting diode technology in which the LED chip is mounted upside down on the substrate. In traditional LED packaging, electrical connections are made through bonding wires that connect the top of the chip to the external circuit. In Flip Chip LED design, the chip is flipped so that its electrical contacts directly face the substrate. This eliminates the need for wire bonding and creates a more compact, durable, and thermally efficient structure.
In the context of cinematic electronics within the cinema industry, Flip Chip LED plays a crucial role in high performance display systems, studio lighting panels, LED cinema screens, and digital projection environments. Because cinema applications demand high brightness, accurate color rendering, stable thermal performance, and long operational life, Flip Chip LED technology offers significant advantages compared to conventional LED packages.
The term flip chip refers to the physical orientation of the semiconductor die. Instead of placing the chip upright and using thin wires to connect it, the chip is inverted and directly bonded to the circuit board using conductive bumps. This structure improves electrical conductivity and heat dissipation, both of which are critical for cinematic lighting and display solutions.
How does Flip Chip LED Work?
Semiconductor principle: At its core, Flip Chip LED operates on the same electroluminescence principle as other LEDs. When an electric current passes through a semiconductor junction composed of p type and n type materials, electrons recombine with holes and release energy in the form of light. The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material used, such as gallium nitride for blue and white light.
Flip mounting mechanism: In Flip Chip LED, the semiconductor die is fabricated with metal contact pads on one side. Instead of connecting wires to these pads, tiny solder bumps are placed on them. The chip is then flipped and aligned precisely onto a substrate or printed circuit board. Heat and pressure are applied to create a strong electrical and mechanical bond. This process ensures a short and direct electrical path.
Thermal conduction process: Because the chip is mounted directly onto the substrate, heat generated during operation flows downward into the board and then into a heat sink. This direct thermal path reduces junction temperature, which improves luminous efficiency and extends operational life. In cinema lighting systems where high intensity illumination is required for long hours, effective thermal management is essential.
Optical emission characteristics: The absence of wire bonds on the top surface allows more uniform light emission. The top surface can be coated with phosphor for white light production or combined with optical lenses to control beam shape. In LED cinema screens and professional studio panels, this uniform emission enhances visual consistency and reduces shadowing artifacts.
What are the Components of Flip Chip LED?
LED chip structure: The semiconductor die is the heart of the Flip Chip LED. It is typically made from gallium nitride based materials grown on sapphire or silicon substrates. The die includes active layers where electron hole recombination produces light.
Solder bumps or metal pads: Instead of wire bonds, Flip Chip LEDs use solder bumps or gold bumps placed on the contact pads. These bumps serve as electrical and mechanical connectors between the chip and the substrate.
Substrate or printed circuit board: The substrate supports the flipped chip and provides electrical routing. It may be made from ceramic, metal core printed circuit board, or silicon depending on application requirements. In cinematic electronics, high thermal conductivity substrates are preferred.
Phosphor layer: For white light applications, a phosphor coating is applied either on the chip or on a separate encapsulation layer. The phosphor converts blue or ultraviolet light into broad spectrum white light that is suitable for cinema illumination.
Encapsulation material: A transparent resin or silicone layer protects the chip and enhances light extraction. This material must withstand high temperatures and prolonged exposure to intense illumination.
Heat sink system: Although not always part of the LED package itself, a heat sink is essential in cinematic systems. It dissipates heat away from the LED assembly to maintain stable performance.
What are the Types of Flip Chip LED?
High power Flip Chip LED: These are designed for applications requiring strong illumination such as cinema stage lighting, projection support systems, and LED walls. They can operate at higher current levels and produce intense luminous output.
Mini Flip Chip LED: Used in fine pitch LED displays for cinema screens, mini Flip Chip LEDs offer high pixel density and improved contrast. Their compact structure supports ultra thin display modules.
Micro Flip Chip LED: These are extremely small LED chips used in advanced display technologies such as micro LED cinema panels. They enable high resolution large format displays with excellent brightness and color precision.
RGB Flip Chip LED: These LEDs integrate red, green, and blue chips in a single package. They are widely used in LED cinema screens to create full color imagery with precise color calibration.
COB Flip Chip LED: Chip on board configuration using Flip Chip technology allows multiple chips to be mounted directly on a single substrate. This design is common in high brightness studio lighting panels and cinema flood lights.
What are the Applications of Flip Chip LED?
LED cinema screens: Modern cinema halls are increasingly adopting LED display screens instead of traditional projection systems. Flip Chip LED technology enhances brightness, contrast, and uniformity in these large displays.
Studio lighting systems: Film production studios require stable, flicker free, and color accurate lighting. Flip Chip LEDs provide high efficiency and reduced thermal stress, making them ideal for long shooting sessions.
Architectural cinema lighting: Theaters, multiplexes, and film festival venues use decorative and ambient lighting. Flip Chip LEDs ensure consistent performance with lower maintenance.
Projection auxiliary lighting: In hybrid projection environments, auxiliary lighting systems rely on durable and efficient LEDs. Flip Chip design supports reliable operation.
Control room displays: Cinematic electronics include monitoring and control panels. High resolution LED displays using Flip Chip technology deliver sharp and vibrant visuals.
What is the Role of Flip Chip LED in Cinema Industry?
Enhancing image brightness: Cinema screens must deliver high brightness levels to ensure clear visibility even in large auditoriums. Flip Chip LED enables higher current handling and improved luminous efficiency.
Improving color accuracy: Accurate color reproduction is essential in filmmaking and screening. Flip Chip LEDs provide stable optical output, supporting better color calibration in RGB systems.
Supporting long duration operation: Cinema halls operate for extended hours daily. The improved thermal path of Flip Chip LEDs reduces degradation and ensures consistent performance over time.
Reducing maintenance costs: Without fragile wire bonds, Flip Chip LEDs are mechanically stronger. This durability reduces the frequency of replacements in cinema installations.
Enabling next generation displays: Advanced LED cinema screens and micro LED panels rely on Flip Chip technology for high pixel density and seamless integration.
What are the Objectives of Flip Chip LED?
To improve thermal management in high power lighting systems.
To eliminate wire bonding related failures and enhance structural strength.
To increase luminous efficiency by reducing internal resistance.
To support compact and high density LED packaging for display technologies.
To ensure stable performance in demanding cinematic environments.
To enhance reliability and lifespan for professional cinema applications.
What are the Benefits of Flip Chip LED?
Higher thermal efficiency: Direct contact between the chip and substrate allows better heat dissipation, which is critical in high brightness cinema lighting.
Greater mechanical reliability: The absence of bonding wires reduces the risk of mechanical breakage during vibration or thermal expansion.
Improved light extraction: The top surface remains unobstructed, allowing more uniform light output.
Compact design: Flip Chip LEDs occupy less space, enabling thinner display panels and lighting modules.
Longer operational life: Lower junction temperature extends the lifespan of the LED.
Energy efficiency: Reduced electrical resistance leads to improved power conversion efficiency.
What are the Features of Flip Chip LED?
Direct chip attachment technology that eliminates wire bonds.
Low thermal resistance design suitable for high power operation.
High luminous output suitable for large format displays.
Compatibility with mini LED and micro LED architectures.
Enhanced structural integrity for professional installations.
High reliability under continuous operation conditions.
Uniform light emission surface ideal for cinematic display panels.
What are the Examples of Flip Chip LED?
Samsung Onyx LED cinema screen: Developed by Samsung Electronics, this cinema screen technology uses advanced LED modules that incorporate Flip Chip structures for high brightness and contrast in commercial theaters.
Sony Crystal LED display: Created by Sony Corporation, Crystal LED panels utilize fine pitch LED modules that benefit from Flip Chip architecture to deliver seamless cinematic visuals.
COB LED studio panels: Many professional lighting manufacturers integrate Flip Chip LEDs into chip on board modules used in film production studios.
Micro LED cinema prototypes: Research and development teams worldwide are implementing Flip Chip micro LED arrays for future cinema display systems.
What is the Definition of Flip Chip LED?
Flip Chip LED is defined as a light emitting diode in which the semiconductor die is mounted upside down onto a substrate using conductive bumps instead of traditional wire bonds, resulting in improved thermal performance, mechanical strength, and electrical efficiency.
What is the Meaning of Flip Chip LED?
The meaning of Flip Chip LED refers to both its physical configuration and its technological advantage. The term flip indicates that the chip is inverted before mounting. The term chip represents the semiconductor die that generates light. Together, Flip Chip LED describes an LED package where the die is flipped and directly connected to the circuit board to enhance performance.
In cinematic electronics, this meaning extends to a broader concept of reliability, precision, and innovation in lighting and display systems.
What is the Future of Flip Chip LED?
Advancement in micro LED cinema displays: Future cinema screens are expected to adopt micro LED panels with Flip Chip structures for ultra high resolution and seamless modular design.
Integration with smart control systems: Flip Chip LEDs will be integrated with intelligent lighting controls for dynamic brightness and color adjustments in theaters.
Higher energy efficiency standards: As the cinema industry aims to reduce energy consumption, Flip Chip LED technology will support more efficient lighting solutions.
Improved manufacturing techniques: Automated flip bonding and wafer level packaging will reduce production costs and enhance scalability.
Expanded role in immersive environments: Virtual production studios and immersive LED volumes will increasingly depend on high performance Flip Chip LED arrays.
Summary
- Flip Chip LED is an advanced LED packaging method where the chip is mounted upside down on the substrate.
- It eliminates wire bonding and improves electrical and thermal performance.
- It offers higher brightness and better reliability for cinematic applications.
- It supports mini LED and micro LED technologies used in modern cinema screens.
- It enhances color accuracy and uniformity in studio lighting and display systems.
- It reduces maintenance and operational costs in cinema installations.
- It represents a key technology shaping the future of cinematic electronics and the cinema industry.